HighDi explains - what you always wanted to know about LED's ...
The development of LEDWhen did it all start? What happened next? Read the full story in our blog.
|
|
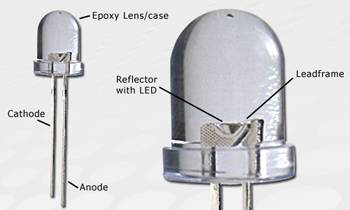
A wired LED (standard LED) consists of the following components: a semiconductor device, a reflector, a cathode, an anode and a plastic lens. The semiconductor device (e.g. Silicon) is soldered on the
bottom of a cone-shaped recess. The inside of the groove serves as a
reflector when current is flowing. For the electrical connection tinned
steel is used, the longer legs of the LED represents the positive pole
(anode) and the shorter legs of the LED negative pole (cathode). The
reflector with the semiconductor device is connected by the solder
joint with the cathode. By a thin connecting wire (bonding wire) the
upper surface of the semiconductor device is connected to the anode. To
fix all the components an LED is surrounded with a plastic lens (see
picture). Which other LED's are there? Read the full story in our blog.
|
|
The spectrum of visible light covers only a very small range of about 370nm (violet) to 760nm (red). Due
to the very compact design and the large color spectrum LED’s are
specialists for white and colored light. Your imagination how to use
LED’s are set no bounds for example, architectural lighting, in
restaurants, bars and discos, as an effect in illuminated advertising,
in your home, garden, at work, building sites and much more. The
light-emitting color of an LED is dependent on the composition of the
installed semiconductor material. There are light radiation in the near
UV, generated in the visible or in the infrared range. The first
commercial LED's lit blue. Here was silicon carbide used as
semiconductor material. Would you like to know more? Read the full story in our blog.
|
| back to help center |
 The
term LED is an indispensable part of today's language. But very few
people know about the development of "Light Emitting Diode" - short
LED. Learn interesting facts about the LED. Enjoy the high quality LED technology with its long lifespan. Enjoy the high quality LED technology with its long lifespan. Please find our fantastic LED product range in our
The
term LED is an indispensable part of today's language. But very few
people know about the development of "Light Emitting Diode" - short
LED. Learn interesting facts about the LED. Enjoy the high quality LED technology with its long lifespan. Enjoy the high quality LED technology with its long lifespan. Please find our fantastic LED product range in our